Turkey’s Struggle with Foreign Terrorist Fighters: How to struggle with the toxic harmonization in its region?
[1] Yeşiltaş, M., Özdemir, Ö. B., Öncel, R., Düz, S. & Öztürk, B. (2016). Sınırdaki düşman: Türkiye’nin DAİŞ ile mücadelesi. SETA Rapor. No: 65. İstanbul: Turkuvaz Haberleşme ve Yayıncılık, p.6.
FTFs are defined as a growing threat to world security. In the light of this definition, countries have been combating against terrorist organizations’ recruitment mechanisms and Foreign terrorists’ transportation. In that regard, countries, including Turkey, has been taking strict measures to fight against this threat. The measures are focusing on preventing radicalization of individuals. Turkey is one of the key countries in this prevention mechanism.
Turkey’s location, as a neighbor of Syria and Iraq, makes it a “transit country” for FTFs trying to reach the two countries. In other words, the country is a “transit hub” for FTFs in their movement and path as reaching the destination. In the light of this information, Turkey’s responsibility is more than others. On the one hand, Turkey, has certain challenges in this subject as a key transit country. For example, through 150km border between Turkey and Syria, 60% of FTFs entered Syria.[1] As a result of its proximity to Syria and Iraq, many security challenges, including YPG/PYD and DAESH/ISIS, have arisen on its borders. However, there are also other terrorist organizations pose a threat, as well. On the other hand, Turkey has a huge capability and capacity to prevent dissemination of radicalism and extremism while FTFs movement to Iraq and Syria to join terrorist organizations. Under these circumstances, Turkey has exerted great efforts to implement preventive procedures and take strong measures to stop their movement.
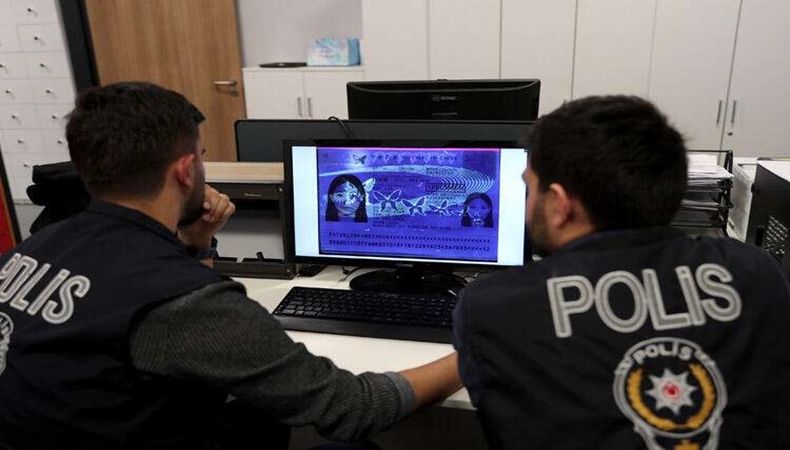
In Turkey’s circumstances, internal security is also significant while fighting against FTF and radicalism. Particularly, Turkey has focused on internal security implications to detect suspicious people and terrorist fighters because it is the country which is affected by this security threat at most. In that regard, police forces have been carefully investigating law enforcements. For example, many terrorist fighters who have a strong relation with DAESH/ISIS were detected. In other words, it is argued that Turkey has an efficient security policy to prevent and combat FTFs. However, DAESH/ISIS attacks in Turkey may put pressure on “well-functioning internal security” because Turkey has been threatened more than rest of the world. According to Yalçınkaya[2],
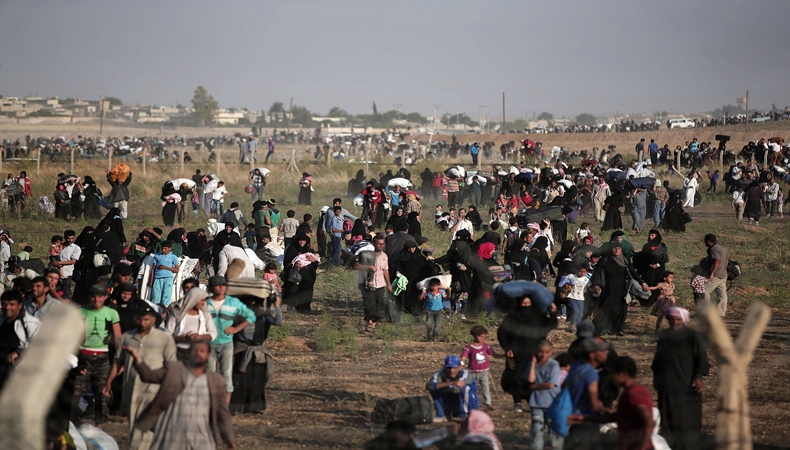
Turkey may have the same problems which the Western countries have, such as FTF returnee, their orientation, disarmament and replacement. Moreover, in addition to these challenges, Turkey is also targeted by terrorist countries at the high level. In that regard, Turkey’s threat has two more dimensions: its concern starts with any FTF deciding to leave his/her hometown and turning back to his/her country. For example, the terrorist fighter mostly passes through Turkey when deciding to reach the source country. During this travel, he or she has a possibility to organize terrorist attack in Turkey. In. March 2014, the terrorist fighter attacked and killed three Turkish citizens while returning to his country. It poses a significant threat, in that regard. It, as a Muslim-majority country, has deeply affected by the power vacuums taking place in other “Muslim-majority” countries because of easy adaptation of high number of Muslim asylum-seekers and refugees fleeing from the instability in their living place. Moreover, local society is also familiar to those refugees’ life because of their locations’ proximity. In that regard, it is highly attractive place to resident for terrorist fighters. As a result of this mutual interaction, it is possible to talk about millions of Syrian refugees living in Turkey. Another reason of this dimension is the stuck of FTFs in Turkey while using illegal passports and identities because the source country cancels his/her citizenship. In that regard, Turkey has to host this terrorist fighter but it leads to increase the country’s vulnerability to terrorist attacks. In that regard, this issue represents an obstacle for Turkey’s liberal visa regime; also, their number is increasing because of this regime. More than 35 million tourists have been annually received by Turkey from different countries. However, under these circumstances, security check points have gained more importance. Turkey’s visa policy is mostly related to tourism and economy. Also, it is important for the globalized world and its economy. In this subject, Syrian policy which has been implemented for years is another problem because of their close ties with PKK terrorist groups. The border, thus, has more meaning that it physically represents. The border should also carefully be checked not only because of terrorist attacks but also smuggling activities of terrorist fighters. In other words, Turkey is under a security threat because of many different reasons which are expressed in this paragraph.
Turkey, as an active member of combat against terrorism and FTF commission, has different responsibilities to contribute global combat against radicalism and extremism. The most significant part of this combat is to prevent mobility of terrorist fighters. Turkey, as a country having significant experience in combat against terrorism, has been conducting this security policy successfully through the Turkish National Police. Moreover, the dissemination of ideology is another dimension of Turkey’s fight against FTFs. Turkey, thus, has two main programs in its fight against FTFs and dissemination of radicalism through terrorist fighters: the Turkish National Police (TNP) and Turkish Government’s Religious Affairs Office. Firstly, TNP is responsible from providing security awareness in the society through effective security measures and training activities. Moreover, they have focused on integration of FTFs into the society through social activities and implementations. Also, they exert utmost effort to reach the suspicious people who pose a significant threat for Turkey’s peaceful atmosphere. Another appreciated activity is to train lecturers and significant religious motives who will be at the forefront in Turkey’s fight against FTFs and radicalism. Through these training mechanisms, Turkey aims to prevent recruitment mechanisms of DAESH/ISIS terrorist groups. The Turkish Government’s Religious Affairs Office (Diyanet) is another branch of Turkey’s combat. This office mainly focuses on countering extremism and radicalism through dissemination of religious facts. In that regard, imams are significant actors to prevent dissemination of radical religious motives. In other words, it is aimed that people having possibility to join these terrorist organizations with the religious motives are educated by imams through first-hand information. In that regard, the number of people joining DAESH/ISIS can be decreased as a result of these educations and social programs.
As a result of these challenges stemming from FTFs and radicalism, Turkey has to develop and take strict security measures. In that regard, its border is the most significant subject on its agenda. In that regard, it produces “non-entry list” by sharing information through other countries despite strong distrust between the EU and Turkey. This is related to share correct information regardless of political disagreements. Mutual trust and information sharing are the essentials in controlling and preventing intensifying flows of FTFs. Moreover, airport control is the important step in this prevention mechanism. Especially, airports in İstanbul are transit hubs for the people. In that regard, police forces are responsible from this part of Turkey’s security policy. Risk Analysis Units mechanism which has been established by Turkey to prevent movements of FTFs is successfully conducted. During cross-border process of terrorist fighters, illegal movements have been detected through this control mechanism. Thus, Turkey is able to prevent the flow of FTFs just on its border. Besides internal measures, international relations and mechanisms are important to eradicate this security threat. International organizations have a significant role, as well. Turkey, as a member of NATO and UN as well as OSCE, have been actively participating in international security measures’ practices. The UN resolution have been adopted related to FTFs are also supported by Turkey. Moreover, it, as a member of Interpol, has a strong information sharing network in this matter. Thus, FTFs can be detected on the border-crossing points thanks to Turkey’s efforts and earlier experiences on terrorism.
As a key transit country, Turkey has exerted great efforts to eradicate FTFs threat. Because of its geographical position, its cooperation is certainly essential in this fight. In that regard, Turkey, heavily affected by this security threat, has taken a noteworthy role in prevention of movement of terrorist fighters and their assets. From the perspective of other countries, Turkey locates in a region with toxic harmonized relations representing links between FTFs and radicalization. However, its security policy has been well-conducted; thus, the number of Turkish origin FTFs and terror attacks organized by Turkish FTFs can be remained at a low level through utmost efforts of Turkish security forces and government’s noteworthy implications.
[1] Hackensberger, Alfred, “Wie die Geheime Allianz mit dem IS zu Bruch Ging”, Die Welt, 24 July 2015 www.welt.de/politik/ausland/article/144423834/Wie-die-geheime-Allianz-mit-dem-IS-zu-Bruch-ging.html.
[2] Yalçınkaya, Haldun. “Turkey’s Struggle Against the Foreign Terrorist Fighters of DAESH”, Perceptions: Journal of International Affairs 21.1 (2016): 27-44.

